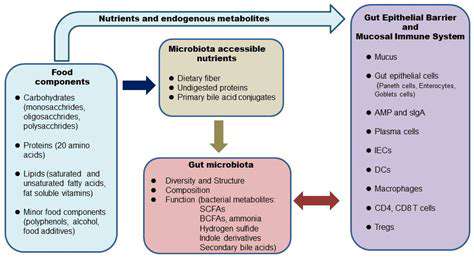
Understanding the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms residing in our digestive tract, plays a crucial role in overall health. Its composition, influenced by factors like diet, genetics, and environmental exposures, significantly impacts how our bodies digest food, absorb nutrients, and even regulate our immune system. Understanding the unique makeup of an individual's gut microbiome is therefore essential for personalized nutrition strategies.
Analyzing this diverse community, often referred to as the microbiota, involves sophisticated techniques like 16S rRNA gene sequencing. This method allows researchers to identify and quantify the different bacterial species present. By comparing these profiles across individuals, we can begin to understand the variations that contribute to different health outcomes and responses to various dietary interventions.
Methods for Analyzing Gut Microbiome Composition
Several advanced laboratory techniques are employed to analyze gut microbiome composition. These methods go beyond simply identifying the presence or absence of bacteria; they aim to quantify the abundance of various species and assess the overall diversity of the microbial community. This detailed information is essential for understanding how the microbiome functions and interacts with the host.
Advanced sequencing technologies, coupled with bioinformatics tools, provide a comprehensive picture of the microbial landscape. These tools allow researchers to identify not only the dominant bacterial species but also the less abundant ones, which might still play critical roles in gut health. Furthermore, metagenomic analyses can reveal the functional potential of the microbiome, offering insights into the metabolic pathways available to the community.
The Impact of Diet on Gut Microbiome Composition
Diet is a powerful determinant of gut microbiome composition. The types of foods we consume significantly affect the types of microorganisms that thrive in our gut. A diet rich in fiber, particularly prebiotic fibers like inulin and oligosaccharides, can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, fostering a healthier gut microbiome. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can negatively impact microbial diversity and potentially contribute to imbalances in the gut ecosystem.
Different dietary patterns, including vegetarian, vegan, or omnivorous approaches, can lead to distinct gut microbiome profiles. This highlights the importance of individualized dietary recommendations tailored to an individual's specific microbiome composition. Furthermore, understanding the effects of specific food components on the microbiome can pave the way for dietary interventions that enhance health and well-being.
Establishing clear and comprehensive AI governance principles is crucial for ensuring regulatory compliance. These principles should outline ethical considerations, data security protocols, and accountability measures for AI systems. They serve as a roadmap for developers, operators, and users of AI technologies, guiding them towards responsible and compliant practices. Furthermore, these principles should be consistently reviewed and updated to reflect evolving technological advancements and regulatory landscapes.
Monitoring Progress and Adapting the Plan: A Dynamic Approach
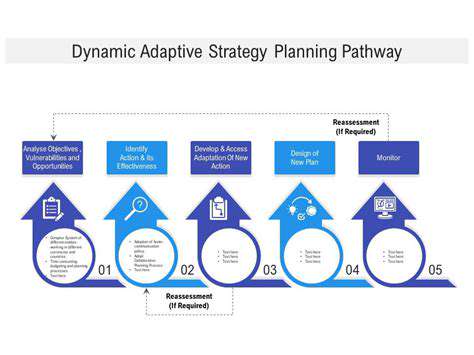
Tracking Key Metrics
Monitoring the progress of any project requires a clear understanding of the key metrics involved. This involves defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals and then consistently tracking data related to those goals. Regular reporting and analysis are crucial for identifying trends and patterns that may indicate potential roadblocks or opportunities for improvement. Without a systematic approach to tracking these metrics, it's difficult to assess whether the project is on track to achieve its objectives.
Different projects will have different key metrics. For example, a marketing campaign might track website traffic, conversion rates, and customer engagement, while a software development project might focus on lines of code written, bug resolution rates, and user feedback.
Identifying Potential Issues
Regular reviews of progress against established metrics are essential to proactively identify potential issues. By analyzing the data, teams can pinpoint areas where the project is falling behind schedule, exceeding budget, or not meeting quality standards. Early identification of these issues allows for timely intervention and mitigation strategies to be implemented before they escalate and significantly impact the project's success.
Thorough analysis of the data is key to understanding the root cause of any identified issues, rather than just reacting to symptoms. This helps avoid repeating mistakes and improves the overall project management process.
Adapting Strategies Based on Findings
Once potential issues are identified, teams need to adapt their strategies to address them effectively. This may involve adjusting timelines, reallocating resources, or modifying project scope, depending on the nature of the problem. Flexible and adaptable strategies are critical to navigating the unexpected challenges that can arise during the project lifecycle.
Adaptability is not just about responding to problems, but also about seizing new opportunities that may emerge. A willingness to change course when necessary can lead to improved outcomes and greater efficiency.
Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration between team members are crucial for successful project adaptation. Open communication channels facilitate the sharing of information, allowing for a collective understanding of issues and potential solutions. Open communication ensures that everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.
Resource Allocation and Management
Managing resources effectively is vital for adapting to changing project needs. This involves being flexible in allocating time, budget, and personnel to address emerging challenges and opportunities. A robust resource management system ensures that the necessary resources are available when and where they are needed.
Proactive resource management minimizes the impact of unforeseen delays or setbacks.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
A thorough risk assessment process is crucial for anticipating and mitigating potential problems. Identifying potential risks helps to understand their likelihood and impact, allowing the project team to develop mitigation strategies in advance.
This proactive approach to risk management reduces the likelihood of unexpected disruptions and allows for a more controlled and predictable project execution.
Continuous Improvement
The process of monitoring progress and adapting to challenges should be seen as an opportunity for continuous improvement. Analyzing what worked well and what could be improved helps refine project management strategies for future endeavors. By learning from each project, teams can develop a more efficient and effective approach to handling future tasks.
Regularly evaluating project outcomes and identifying areas for improvement contributes to a culture of continuous learning and advancement within the organization.