Introduction to Sustainable Agriculture for Small Farms
Understanding the Principles of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture for small farms goes beyond mere food production; it's about cultivating a resilient farming ecosystem that harmonizes with nature while ensuring long-term economic stability. This methodology emphasizes ecological equilibrium, reducing dependency on artificial inputs like synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and optimizing natural resources. Core strategies such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management work synergistically to improve soil vitality, conserve water, and minimize farming's environmental impact.
Embracing these principles fosters a more diverse and robust farm environment. By nurturing healthy soil and encouraging beneficial microbial activity, farmers can decrease their reliance on chemical products, leading to reduced operational costs and enhanced profitability over time. This system also bolsters biodiversity, supporting a wider array of pollinators and beneficial insects, ultimately creating a more sustainable agricultural model.
Implementing Sustainable Practices on Small Holdings
Transitioning to sustainable methods on small farms demands thoughtful planning and gradual implementation. Farmers should evaluate current operations, pinpoint areas for enhancement, and develop customized strategies that align with their unique resources, climate conditions, and market opportunities. This process often involves testing various techniques, including composting, water conservation methods, and crop diversification to mitigate pest and disease risks.
Soil health improvement stands as a cornerstone of sustainable farming. Techniques like cover cropping enhance soil structure, boost organic content, and naturally suppress weeds. Equally important is crop diversification. Planting multiple crop varieties in a single field increases biodiversity, decreases pest vulnerability, and strengthens overall farm resilience.
Economic Viability and Market Access
Sustainable agriculture offers both environmental and economic benefits. By minimizing expensive external inputs, farmers can reduce costs and improve profit margins. Additionally, the rising consumer demand for sustainably grown food creates opportunities to access premium markets and command higher prices. Direct sales channels like farmers' markets and online platforms help establish loyal customer bases and more stable income streams.
Numerous support programs exist to assist small farmers in adopting sustainable methods, offering financial aid, technical expertise, and market access. Exploring value-added opportunities, such as food processing or preservation, can further enhance marketability and farm income.
Challenges and Considerations for Small Farm Sustainability
While sustainable agriculture presents numerous advantages, small farms often encounter unique implementation challenges. Limited resources, information access, and the need to balance environmental concerns with financial realities can pose significant hurdles. Farmers may need to invest in new equipment, acquire specialized knowledge, or navigate complex regulations. However, various resources and support networks exist to help overcome these obstacles.
Maintaining equilibrium between profitability and environmental responsibility remains crucial. Farmers must consider long-term sustainability objectives while ensuring current operations remain economically viable. This often involves creatively integrating sustainable practices into existing systems while staying informed about agricultural advancements.
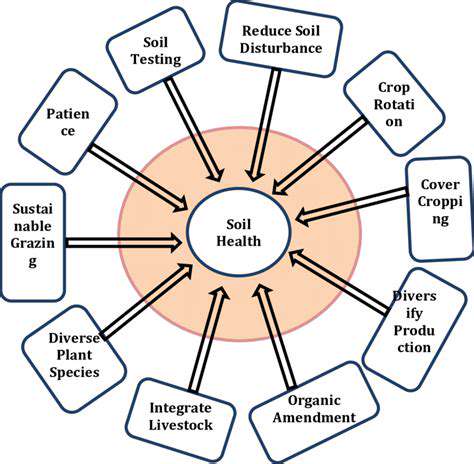
Water Conservation Techniques for Efficient Irrigation
Understanding Water Needs of Crops
Different crops have varying water requirements, influenced by species characteristics, growth stages, and environmental factors. Proper assessment of these variables, along with soil type, climate, and rainfall patterns, enables farmers to develop precise irrigation strategies that minimize waste while maximizing yields. Thorough understanding of crop water needs throughout their life cycles forms the foundation for sustainable irrigation planning.
Selecting Appropriate Irrigation Methods
Various irrigation systems offer different water efficiency benefits. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, dramatically reducing evaporation and runoff. While sprinkler systems cover larger areas, they're generally less precise. The optimal method depends on specific crop requirements, land characteristics, and water availability. Choosing systems that minimize environmental water loss is paramount for conservation efforts.
Implementing Efficient Irrigation Scheduling
Precise irrigation timing is essential for water conservation and optimal plant growth. Monitoring soil moisture and weather patterns allows for adjustments in watering frequency and duration. Automated systems can enhance this process, ensuring water application only when necessary. Regular soil moisture checks enable farmers to deliver water precisely when plants need it most, reducing waste and promoting healthy growth.
Utilizing Drought-Resistant Crops
Incorporating drought-tolerant varieties significantly reduces irrigation demands. These naturally resilient crops adapt well to low-rainfall conditions, decreasing the need for supplemental watering. Selecting appropriate varieties for local climates optimizes water use efficiency and minimizes environmental strain. This approach proves particularly valuable in water-scarce regions, helping maintain agricultural productivity despite challenging conditions.
Water Harvesting and Recycling Techniques
Rainwater collection and greywater reuse provide practical solutions for increasing irrigation water supplies. These methods conserve freshwater resources and reduce groundwater dependence. Recycling irrigation runoff further enhances water efficiency. Such techniques contribute to more resilient agricultural systems, especially in areas with limited water availability.
Soil Moisture Monitoring and Management
Regular soil moisture assessment enables precise irrigation scheduling, preventing overwatering and conserving resources. Effective soil management practices, including proper aeration and organic matter incorporation, improve water retention and reduce runoff. These techniques optimize water use efficiency by ensuring moisture remains available to plants when needed.
Promoting Sustainable Irrigation Practices Across Farms
Widespread adoption of water conservation methods requires collaborative efforts within agricultural communities. Knowledge sharing and training programs help farmers implement efficient irrigation systems. Educational initiatives empower growers with skills needed for sustainable water management. This collective approach fosters broader implementation of water-saving techniques, contributing to more resilient agricultural landscapes.
Diversification and Value Addition for Enhanced Profitability
Diversifying Crop Production for Increased Revenue
Crop diversification beyond traditional staples enhances agricultural sustainability and profitability. Incorporating high-value crops alongside staple foods reduces dependence on single commodities, mitigating risks from pests, diseases, and market volatility. Exploring niche markets for specialty crops like organic or heirloom varieties can further boost income potential when aligned with consumer demand.
Value Addition Through Processing and Packaging
Transforming raw produce into value-added products significantly increases revenue potential. Processing techniques like drying, canning, or preserving enable farmers to capture greater market value. Quality packaging not only enhances product appeal but also reduces spoilage during transport and storage, ultimately contributing to higher profitability and customer satisfaction.
Integrating Livestock for Synergistic Benefits
Combining livestock with crop production creates mutually beneficial relationships. Animals can utilize crop residues as feed, reducing waste and external feed costs. Livestock manure serves as natural fertilizer, enhancing soil health while decreasing synthetic fertilizer dependence. This integrated approach maximizes resource utilization within the farming system.
Implementing Efficient Water Management Practices
In water-scarce regions, efficient irrigation methods like drip systems significantly reduce consumption while maintaining yields. These techniques conserve precious resources while lowering operational expenses, contributing to both environmental sustainability and economic viability.
Optimizing Farm Management Practices for Increased Productivity
Adopting precision agriculture tools, including GPS technology and soil sensors, enables data-driven decision making. These technologies optimize resource allocation, minimize waste, and boost efficiency. Sustainable practices like crop rotation and integrated pest management further enhance long-term productivity while reducing chemical inputs.
Building Sustainable Relationships with Consumers and Markets
Direct marketing through farmers' markets, online platforms, or CSA programs allows farmers to establish personal connections with consumers. Highlighting sustainable production methods can attract environmentally conscious buyers willing to pay premium prices. Understanding and responding to consumer preferences helps farmers develop loyal customer bases and more stable income streams.