Defining Sustainable Food Procurement
Defining Sustainable Food Procurement
Sustainable food procurement is a crucial aspect of modern food systems, encompassing a wide range of practices that aim to minimize the negative environmental and social impacts of food production and consumption. It involves a conscious effort to select and source food products that are environmentally friendly, socially responsible, and economically viable. This approach moves beyond simply focusing on price and availability, prioritizing factors like fair labor practices, reduced carbon footprint, and preservation of biodiversity in the supply chain.
A key component of sustainable food procurement is the consideration of the entire lifecycle of a food product, from farm to table. This includes evaluating the environmental impact of farming practices, transportation methods, and packaging materials. It also encompasses ethical considerations, such as fair wages and safe working conditions for farmworkers and other individuals involved in the food supply chain. In essence, it's about making conscious choices that support a more resilient and equitable food system.
Key Principles of Sustainable Food Procurement
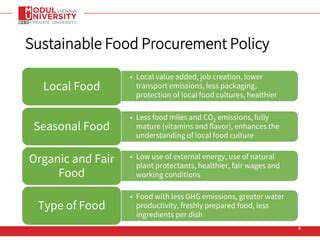
Sustainable food procurement is built upon several core principles, including minimizing environmental impact. This means seeking out products with lower carbon footprints, reduced water usage, and minimal waste generation throughout their lifecycle. Prioritizing local and regional sourcing is another vital aspect, contributing to reduced transportation costs and emissions, and supporting local farmers and economies.
Another key principle is promoting social responsibility. This involves ensuring fair labor practices throughout the entire supply chain, from farm workers to processing facilities and retailers. It also means supporting small-scale farmers and producers, ensuring fair prices and equitable market access.
Finally, economic viability is also paramount. Sustainable procurement strategies should consider the long-term financial implications of purchasing sustainable food products, balancing cost with quality and social responsibility.
Benefits of Sustainable Food Procurement
Adopting sustainable food procurement practices offers a multitude of benefits, both for organizations and the wider community. By reducing the environmental impact of food procurement, organizations can improve their brand reputation and enhance their image as socially responsible entities. Organizations can also realize cost savings by optimizing supply chains and reducing waste.
Ultimately, sustainable food procurement contributes to a more resilient and equitable food system, supporting local communities, preserving biodiversity, and fostering a healthier planet for future generations. This approach extends beyond simple cost-effectiveness to encompass a commitment to ethical and environmentally sound practices.
By integrating sustainable procurement principles into their purchasing policies, organizations can significantly contribute to a more sustainable future for all.
Strategies for Implementing Sustainable Procurement

Sustainable Practices in Supply Chains
Implementing sustainable practices within supply chains is crucial for minimizing environmental impact and promoting social responsibility. This involves a shift from traditional, often unsustainable, models to ones that prioritize resource efficiency, waste reduction, and ethical labor practices throughout the entire value chain. Companies must assess their current supply chain practices, identifying areas where improvements can be made. This includes evaluating the sourcing of raw materials, transportation methods, manufacturing processes, and the handling of waste products. A thorough understanding of the entire supply chain allows for the development of targeted strategies for sustainability.
Implementing sustainable supply chains requires a collaborative effort between all stakeholders, from suppliers and manufacturers to retailers and consumers. Open communication and transparency throughout the chain are essential to ensure everyone is aware of the sustainability goals and how they can contribute. This includes establishing clear metrics for measuring progress, providing incentives for sustainable practices, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Technological Advancements for Enhanced Sustainability
Technological advancements play a significant role in supporting the implementation of sustainable practices in supply chains. Automation and data analytics can optimize logistics, reducing transportation costs and emissions. Using sensors and IoT devices allows for real-time monitoring of inventory levels and resource consumption, leading to more efficient resource allocation and reduced waste. Furthermore, the development of sustainable materials and innovative manufacturing processes are transforming industries, making them more environmentally friendly.
The use of blockchain technology offers enhanced transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain. This enables businesses to track products from origin to consumer, ensuring ethical sourcing and minimizing the risk of counterfeit goods. By leveraging technology, companies can gain greater insights into their environmental footprint and identify opportunities for improvement across all stages of the supply chain.
Financial Incentives and Policy Support for Sustainability
Financial incentives and supportive policies can play a crucial role in driving the adoption of sustainable practices in supply chains. Subsidies for the development and implementation of sustainable technologies, tax breaks for companies that prioritize environmental stewardship, and regulations that incentivize sustainable practices can significantly accelerate the transition. Governments can also play a vital role in establishing clear environmental standards and providing resources for businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
Incentives, such as tax credits for renewable energy investments, can incentivize companies to adopt greener practices. Government regulations can mandate specific sustainability standards, ensuring that companies meet certain environmental criteria. By combining financial incentives with supportive policies, governments can create a favorable environment for businesses to embrace sustainability and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Measuring and Monitoring Success
Defining Success Metrics
Success in sustainable food procurement for universities isn't solely about reducing environmental impact. A comprehensive approach considers a range of interconnected factors, including cost savings, supplier relationships, student and staff engagement, and the overall impact on the local community. Developing clear, measurable metrics for each of these areas is crucial for tracking progress and demonstrating the value of the initiative. This might involve quantifying reductions in food waste, analyzing the carbon footprint of sourced ingredients, and evaluating feedback from student surveys about the quality and variety of sustainable food options.
Establishing baselines for each metric is essential before implementing any changes. This baseline data provides a crucial benchmark against which future progress can be measured and evaluated. A well-defined framework for measuring success ensures that the university's sustainability goals are not just aspirations, but actionable and measurable targets.
Quantifying Environmental Impact
A key aspect of measuring success in sustainable food procurement is quantifying the environmental impact of the university's food choices. This includes evaluating the carbon footprint of different food sources, assessing water usage in agriculture, and analyzing the overall ecological impact of the supply chain. Using data-driven methodologies, such as life-cycle assessments (LCAs), allows universities to gain a deeper understanding of the environmental footprint associated with different procurement decisions. These analyses provide essential insights for prioritizing sustainable practices and making informed choices about sourcing and ingredient selection.
Analyzing Financial Implications
Sustainable food procurement strategies can offer significant cost savings over time. By optimizing supply chains, reducing waste, and leveraging local partnerships, universities can potentially lower their overall food costs. Understanding the financial implications of different procurement strategies is essential for demonstrating the long-term economic viability of sustainability initiatives. This includes analyzing the costs associated with sustainable packaging, transportation, and sourcing options, as well as potential savings from reduced waste.
Analyzing the return on investment (ROI) of sustainable food procurement initiatives is important. This includes looking at the cost savings and the potential for increased revenue from new product lines and partnerships. Such financial analyses help to demonstrate the value proposition of sustainable food procurement to stakeholders and secure continued support for the initiative.
Evaluating Stakeholder Engagement
Successful sustainable food procurement initiatives require the engagement and participation of all stakeholders. This includes students, faculty, staff, and even community members. Gathering feedback from these groups is essential to understanding their needs, preferences, and concerns regarding sustainable food choices. This can be achieved through surveys, focus groups, and regular communication channels. Assessing stakeholder satisfaction levels and understanding their perceptions of the sustainability initiatives can guide improvements and ensure the program aligns with the broader university community's values.
Monitoring Supplier Relationships
Building strong, reliable relationships with sustainable food suppliers is critical for long-term success. This involves evaluating supplier practices, ensuring ethical sourcing, and supporting local farmers and producers. Monitoring supplier relationships involves regular communication, performance evaluations, and ensuring compliance with sustainability standards. This includes assessing the commitment of suppliers to environmental and social responsibility. Maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is vital for ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of sustainable food products.
Regular audits of supplier practices are essential to ensure ethical and sustainable sourcing. This process helps to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in the supply chain, and to implement corrective actions if needed. Transparency and accountability in supplier relationships are crucial for building trust and maintaining a sustainable food system.