Exploring the Limits of Lab-Grown Meat
The burgeoning field of lab-grown meat, or cultured meat, presents a fascinating glimpse into the future of food production. This innovative approach promises to revolutionize agriculture by offering a sustainable and potentially ethical alternative to traditional methods. This process involves cultivating muscle tissue from animal cells in a controlled laboratory environment, eliminating the need for slaughtering animals. It's a complex process, but one with the potential to significantly reduce our environmental footprint.
While still in its nascent stages, lab-grown meat research is rapidly advancing. Scientists are constantly refining techniques to improve yield, reduce costs, and enhance the texture and flavor of the final product. This ongoing research holds enormous promise for a more sustainable food system.
The Environmental Impact of Lab-Grown Meat
One of the most compelling arguments for lab-grown meat centers on its potential to drastically reduce the environmental impact of animal agriculture. Traditional livestock farming is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. Lab-grown meat, by contrast, promises a significantly lower environmental footprint. The reduced land and water usage associated with this method could be transformative for our planet.
Furthermore, the reduced reliance on antibiotics and hormones in lab-grown meat production could contribute to a healthier ecosystem. The potential for significant environmental benefits makes this research a critical area of focus.
Ethical Considerations in Lab-Grown Meat Production
As with any new technology, lab-grown meat raises important ethical considerations. Concerns surrounding animal welfare are paramount, and proponents must address these concerns openly and honestly. Transparency and careful consideration of the ethical implications are essential as this technology progresses. The potential for misuse and the need for stringent regulations are critical aspects to explore.
The implications of lab-grown meat extend beyond the immediate production process. The transition to this new food system necessitates careful consideration of the long-term economic and social impacts on existing agricultural communities.
Cost and Accessibility of Cultured Meat
Currently, the cost of producing lab-grown meat is significantly higher than that of conventionally raised meat. However, ongoing research and technological advancements are expected to drive down production costs in the future. Over time, this could make lab-grown meat a more accessible and affordable option for consumers.
Several factors contribute to the current high cost, including the specialized equipment and expertise required for cell culture. The long-term goal is to establish efficient and scalable production methods, ultimately making this technology more widely available.
Future Applications and Possibilities
The potential applications of lab-grown meat extend beyond simply replacing traditional meat products. Researchers are exploring the possibility of creating customized meat products with specific nutritional profiles or tailored textures. This opens up exciting avenues for personalized nutrition and tailored food solutions.
Furthermore, the techniques developed for lab-grown meat could be adapted for other applications, such as creating lab-grown leather and other animal products. This opens up a wide range of possibilities for a more sustainable and innovative future.
Environmental Sustainability: A Game Changer for Food Production

Environmental Sustainability: A Growing Concern
Environmental sustainability is a pressing global issue that demands immediate attention. It encompasses a wide range of concerns, from the depletion of natural resources to the escalating threat of climate change. The interconnectedness of these issues highlights the critical need for a holistic approach to environmental stewardship. Addressing environmental sustainability requires a fundamental shift in our consumption patterns and production methods, moving towards a more responsible and eco-conscious way of life. This crucial transition is essential for ensuring a healthy planet for future generations.
The alarming rate at which our planet's resources are being consumed necessitates a profound change in how we interact with the environment. Ignoring these critical issues will have devastating consequences for the planet's ecosystems and the well-being of all living things. This includes everything from the forests and oceans to the air we breathe. We must act now to mitigate the damage already inflicted and to prevent further degradation of our natural resources.
Strategies for a Sustainable Future
A multitude of strategies can be implemented to foster environmental sustainability. These strategies range from individual actions, such as reducing energy consumption and adopting sustainable transportation, to large-scale policy changes, such as investing in renewable energy and promoting sustainable agriculture. The critical importance of education and awareness cannot be overstated. Educating individuals about the environmental impact of their choices is crucial for driving behavioral changes.
Technological innovation plays a significant role in achieving environmental sustainability. Developing and implementing sustainable technologies is vital for reducing our environmental footprint. This includes innovations in renewable energy, waste management, and resource efficiency. These technologies hold the key to mitigating climate change and promoting resource conservation. Furthermore, it is critical to support sustainable businesses and initiatives. Supporting businesses committed to environmental responsibility can propel positive change.
International cooperation and collaboration are essential for tackling global environmental challenges. Sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices across borders is paramount. Global partnerships can accelerate the development and implementation of effective solutions to environmental problems. The interconnected nature of environmental issues underscores the need for collective action and shared responsibility in ensuring a sustainable future for all.
Implementing sustainable practices requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing individual actions, business strategies, and international cooperation. This approach ensures a holistic and effective response to the complex challenges of environmental sustainability. By working together, we can create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Deepfakes, synthetic media that superimposes a person's likeness onto another video or audio, pose a significant threat to individuals and society. The ease with which these forgeries can be created and disseminated is alarming, allowing malicious actors to spread misinformation and disinformation on an unprecedented scale. This technology, while initially developed for creative purposes, has now become a tool for manipulation, potentially undermining trust in established media and institutions.
Ethical Considerations and Consumer Acceptance
Transparency and Traceability
In the rapidly evolving landscape of food innovation, transparency and traceability are paramount. Consumers increasingly demand detailed information about the origin, production methods, and ingredients of their food. This demand extends beyond basic labeling to encompass the entire supply chain, from farm to table. Understanding where food comes from and how it's produced builds trust and allows consumers to make informed choices aligned with their values, whether environmental, social, or ethical.
Traceability systems, incorporating technology like blockchain, can provide detailed records of every step in a food product's journey. This allows for greater accountability, enabling consumers to identify potential ethical concerns or environmental impacts and hold producers responsible for their practices. For example, knowing the specific farm a chicken came from and the feeding practices employed allows consumers to align their purchasing decisions with their values regarding animal welfare.
Animal Welfare and Sustainability
Ethical considerations regarding animal welfare are becoming increasingly important to consumers. The future of food must prioritize humane treatment and sustainable practices in animal agriculture. This includes reducing the environmental impact of livestock farming, improving living conditions for animals, and ensuring responsible sourcing of feed and resources. Consumers are demanding more transparency and accountability in the treatment of animals, leading companies to adopt more ethical and sustainable practices.
Sustainable farming practices are crucial for long-term food security and environmental protection. Innovations in animal husbandry, such as alternative protein sources and precision agriculture, are essential to meet growing demand while minimizing environmental harm. These practices should also consider the social impact on farmers and local communities, fostering a more equitable and sustainable food system.
Food Safety and Allergen Management
Food safety is a fundamental ethical concern, and the future of food must prioritize the health and well-being of consumers. New food technologies, while offering exciting possibilities, require robust safety assessments to ensure they don't pose unforeseen risks. Strict regulations and rigorous testing procedures are essential to prevent foodborne illnesses and protect vulnerable populations. Consumers are rightfully concerned about the potential health implications of new ingredients and processing techniques, requiring clear labeling and transparent communication about food safety protocols.
Advancements in allergen management are also crucial. As food innovation expands the range of ingredients and processing methods, accurate labeling and clear communication about potential allergens are essential to prevent adverse reactions. Consumers with allergies need assurance that food products are properly labeled and handled to minimize the risk of allergic reactions. This necessitates a collaborative effort between food producers, regulatory bodies, and consumers to ensure safe and accessible food options for all.
Consumer Acceptance and Cultural Sensitivity
Consumer acceptance of new food innovations is heavily influenced by cultural values and beliefs. Understanding diverse perspectives and incorporating cultural sensitivity into the development and marketing of new foods is essential. Food innovations should not perpetuate existing inequalities or marginalize specific cultural groups. For instance, when introducing alternative protein sources, consideration should be given to how these options align with existing dietary traditions and cultural preferences.
Cultural sensitivity also extends to the communication of food innovations to diverse audiences. Clear and accessible information about new food technologies and their potential impacts is vital. This includes considering language barriers and cultural nuances when conveying information about food safety, nutritional value, and ethical considerations. Effective communication fosters trust and encourages the adoption of innovations in a responsible and inclusive manner.
The Future of Food: A Multifaceted Approach
Cultivating Innovation in Lab-Grown Foods
The future of food is undeniably intertwined with innovation, and lab-grown meat is a prime example. This burgeoning field is not just about creating alternative protein sources; it's about addressing critical issues like sustainability and ethical concerns surrounding traditional animal agriculture. Producing meat in a controlled laboratory environment drastically reduces the environmental impact associated with livestock farming, including land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. This approach offers a powerful potential for reducing our ecological footprint and ensuring a more sustainable food system for generations to come, while simultaneously providing consumers with palatable and nutritious options.
Beyond meat, lab-grown alternatives are expanding to encompass a wider range of food products, from dairy to seafood. These innovations are not simply about creating substitutes; they're about creating opportunities for tailored nutrition, potentially addressing allergies and dietary restrictions. Scientists are exploring ways to customize the nutritional profile of these lab-grown products to meet the specific needs of individual consumers, paving the way for a future where food is more accessible and tailored to individual preferences. The potential benefits extend beyond dietary flexibility. The possibilities for optimizing the composition of these foods to improve overall health and well-being are vast.
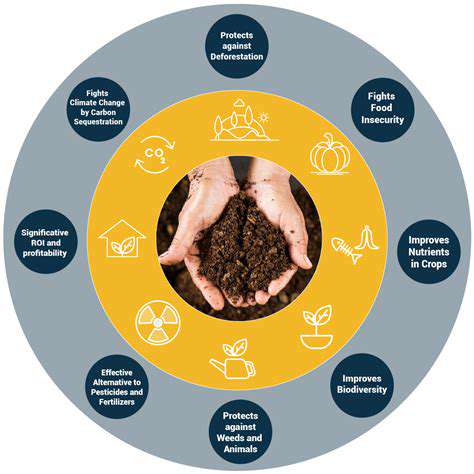
Addressing Global Food Security Challenges Through Precision Agriculture
As the global population continues to grow, ensuring food security for everyone becomes increasingly critical. Precision agriculture, leveraging technology and data analysis, plays a crucial role in optimizing crop yields and resource utilization. Employing sensors, drones, and sophisticated software, farmers can gather real-time data on soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns, allowing for highly targeted interventions and optimized resource allocation. This data-driven approach ensures that resources like water and fertilizers are used efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing crop output in challenging environments.
Furthermore, precision agriculture allows for the development of more resilient crops that can thrive in diverse and changing climates. By analyzing genetic data and implementing targeted breeding programs, researchers can create crops that are resistant to pests, diseases, and extreme weather events. This resilience is paramount in the face of climate change, ensuring a stable and reliable food supply in the future. Cultivating food security through precision agriculture is essential in a world grappling with growing populations and increasingly unpredictable weather patterns.
The rise of precision agriculture is not just about increasing yields; it's about creating more sustainable and environmentally conscious farming practices. By optimizing resource use and minimizing waste, we can cultivate a more sustainable food system that safeguards our planet's resources for future generations. The potential for dramatically improving agricultural output while minimizing environmental impact is significant and holds great promise for addressing global food security concerns.