The Complexities of Perimenopause and Nutritional Needs
Understanding the Hormonal Shift
Perimenopause represents a significant transition in a woman's biological journey, characterized by gradual reductions in key reproductive hormones like estrogen and progesterone. These hormonal ebbs and flows create a complex physiological environment that manifests through diverse symptoms, presenting unique challenges for women undergoing this change. Grasping the subtle dynamics between these hormones proves fundamental for successfully managing perimenopause's multifaceted effects.
Varied Symptoms and Their Impact
Perimenopausal symptoms display remarkable variability, from barely noticeable to profoundly disruptive. Common manifestations include sudden temperature fluctuations, nocturnal perspiration, sleep pattern disruptions, emotional volatility, and genital discomfort. These physical and psychological changes can dramatically influence daily functioning, altering rest quality, vitality reserves, and general health perception. Identifying and addressing these symptoms becomes paramount for preserving wellness during this transformative phase.
Impact on Physical Health
The hormonal transitions occurring during perimenopause precipitate several physiological modifications. Potential concerns include diminished bone mineral content, elevated cardiovascular vulnerability, and metabolic alterations. Maintaining nutritional adequacy, consistent physical activity, and transparent dialogue with healthcare providers forms the cornerstone of risk reduction.
This transitional period may also affect lipid profiles and circulatory pressure parameters, potentially increasing susceptibility to chronic conditions. Routine health evaluations and candid discussions with medical professionals about these evolving health considerations remain essential.
Mental and Emotional Well-being
The psychological dimension of perimenopause merits equal attention, as hormonal variations may precipitate mood instability, heightened anxiety, or depressive tendencies. Implementing comprehensive self-nurturing practices, cultivating supportive networks, and potentially engaging therapeutic interventions can provide valuable coping mechanisms during this challenging life chapter.
Management Strategies and Support Systems
Numerous evidence-based approaches exist to mitigate perimenopausal difficulties. Lifestyle adaptations incorporating stress-mitigation methods, regular movement patterns, and balanced nutritional intake can substantially alleviate symptom burden. Establishing connections with empathetic peer networks, whether personal or organized support groups, offers invaluable emotional reinforcement and practical guidance.
Seeking Professional Guidance
While behavioral modifications provide foundational support, professional medical consultation ensures comprehensive perimenopausal management. Qualified practitioners can deliver individualized recommendations, identify potential health complications, and prescribe appropriate interventions. Maintaining transparent communication with healthcare providers facilitates development of customized symptom management protocols, safeguarding overall wellness throughout this natural biological transition. Professional insight often makes the critical difference in navigating this complex life stage successfully.
Essential Nutrients for Hormonal Equilibrium

Protein for Hormone Synthesis
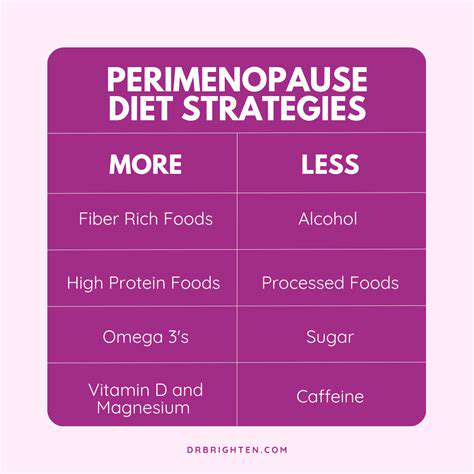
Protein serves as the fundamental substrate for hormone creation, given that numerous hormones originate from amino acid precursors. Optimal protein consumption facilitates production of vital signaling molecules including metabolic regulators, growth factors, and thyroid hormones, all essential for systemic homeostasis. Incorporating diverse protein sources such as lean meats, seafood, legumes, and pulses supports robust endocrine function and physiological processes.
The structural integrity and biological activity of hormones depend heavily on protein quality rather than mere quantity. Selecting complete protein sources guarantees availability of necessary precursors for efficient hormone synthesis and modulation.
Essential Fats for Endocrine Function
Specific lipid categories play indispensable roles in hormone formation and activity. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids constitute structural components of numerous hormones and facilitate optimal endocrine system operation. Regular consumption of lipid-rich foods like avocado varieties, tree nuts, oil seeds, and oily fish promotes hormonal harmony.
These specialized fats transcend culinary properties, serving as critical substrates for hormone generation and regulation, directly influencing the body's endocrine efficiency.
Dietary Fiber for Metabolic Stability
Fiber exerts significant influence over glycemic control, a pivotal factor in endocrine health. High-fiber dietary patterns help modulate blood glucose excursions that might otherwise disrupt hormonal equilibrium. Incorporating diverse fibrous foods including seasonal produce, leafy vegetables, and intact grains contributes to glucose stability and endocrine support.
Complex Carbohydrates for Sustained Vitality
Polysaccharides provide gradual energy release, crucial for maintaining hormonal consistency. Selecting complex carbohydrates rather than refined sugars helps prevent glycemic volatility that impairs endocrine regulation. Nutrient-dense options like whole grain varieties, ancient grains, and tuberous vegetables deliver prolonged energy without abrupt metabolic fluctuations.
These carbohydrate forms provide foundational energy support, preventing fatigue cycles while promoting stable hormone activity.
Micronutrients for Endocrine Support
Various vitamins and minerals participate in critical endocrine processes. Magnesium, zinc, and vitamin D participate in multiple hormonal pathways essential for systemic balance. Consuming varied whole foods including colorful produce, seeds, and fortified items helps ensure sufficient micronutrient intake.
The synergistic relationships between micronutrients significantly influence endocrine health, where deficiencies in one element may cascade into broader hormonal disruptions.
Hydration for Hormonal Transport
Adequate fluid intake proves essential for endocrine operations. Water facilitates hormone circulation and supports metabolic activities central to endocrine regulation. Optimal hydration remains fundamental for hormone distribution and biochemical processes. Consistent water consumption throughout waking hours supports comprehensive endocrine function.
Insufficient hydration may compromise hormonal balance, potentially leading to fatigue, mood alterations, and other physiological disturbances. Maintaining fluid equilibrium underpins overall endocrine health.
Stress Modulation for Hormonal Stability
Persistent stress profoundly affects endocrine equilibrium, potentially triggering systemic imbalances. Implementing stress-reduction techniques including physical activity, mindfulness practices, or nature immersion proves vital for preserving hormonal harmony. Prioritizing stress-management approaches contributes substantially to endocrine well-being.
Chronic stress disrupts delicate endocrine interactions, potentially precipitating various health complications. Adopting effective stress-alleviation strategies helps maintain optimal hormonal function.
Collaborating with Experts for Tailored Guidance
Identifying Qualified Practitioners
Selecting appropriately credentialed professionals for personalized nutritional guidance significantly impacts outcomes. Consider consulting registered dietitians or nutritionists possessing advanced training in nutritional biochemistry. These specialists deliver science-based recommendations customized to individual requirements and health objectives. For cases involving significant endocrine concerns, endocrinology specialists or physicians may provide complementary expertise, offering comprehensive care that addresses both nutritional and medical dimensions.
Investigating local resources, digital platforms, or professional referrals facilitates connections with suitable practitioners. Evaluate credentials, practical experience, and demonstrated competence in individualized nutrition strategies. Client testimonials and professional reviews offer additional insights into practitioner methodologies and effectiveness.
Assessing Individual Requirements
Effective personalized nutrition begins with thorough evaluation of unique physiological needs, lifestyle factors, and personal preferences. This encompasses current health parameters, dietary limitations, daily routines, and specific endocrine-related goals. Compiling detailed medical background information, including existing conditions and therapeutic regimens, ensures development of safe, appropriate nutritional interventions.
Beyond medical considerations, evaluate practical lifestyle elements including occupational demands, physical activity patterns, and stress exposure. Transparent communication with chosen professionals guarantees alignment between recommended strategies and real-world implementation, fostering sustainable health outcomes.
Developing Cooperative Strategies
Creating effective nutritional plans for endocrine balance requires active collaboration between clients and practitioners. Engage fully in the planning process by voicing questions, concerns, and personal preferences. The objective involves formulating approaches that combine scientific validity with practical feasibility and personal satisfaction. This includes establishing achievable targets, comprehending nutritional rationales, and anticipating potential implementation challenges.
Ongoing dialogue and progress evaluation form critical components of this partnership. Prepare to document experiences, monitor advancements, and modify approaches as needed. This adaptive process ensures continued relevance to evolving needs, maximizing the long-term benefits of personalized nutritional support for endocrine health.