Quantum chemistry represents a pivotal branch of chemistry where quantum mechanics principles are harnessed to decode molecular structures, behaviors, and reactions. By examining atomic and molecular interactions at their most fundamental level, this discipline employs sophisticated mathematical frameworks to anticipate and elucidate chemical phenomena. Grasping these core interactions is indispensable for unlocking the secrets of chemical reactivity. Unlike classical mechanics, which falls short in atomic-scale explanations, quantum chemistry provides the necessary depth.
The Role of Technology in Optimizing Sustainability
Technological Advancements in Agriculture
Technological innovations are revolutionizing agricultural practices, allowing for more efficient resource utilization and reduced environmental impact. Precision agriculture, leveraging GPS and sensor technology, enables farmers to tailor their inputs – water, fertilizers, and pesticides – to specific areas and needs. This targeted approach minimizes waste and conserves valuable resources, promoting sustainable farming practices. The development of drought-resistant crops and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) further contributes to increased yields while reducing the need for extensive irrigation and chemical treatments.
Automated systems and robotics are also playing a crucial role in streamlining farm operations. These technologies can optimize planting, harvesting, and post-harvest handling, reducing labor costs and minimizing food waste. Moreover, advancements in livestock management, such as smart feeding systems and automated monitoring, contribute to improved animal welfare and reduced environmental footprint.
Sustainable Packaging Innovations
The packaging industry is increasingly embracing innovative solutions to minimize its environmental impact. Biodegradable and compostable materials are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional plastics. These materials derived from renewable resources decompose naturally, reducing reliance on landfills and minimizing plastic pollution. Companies are exploring innovative packaging designs, such as lightweight and reusable options, to further reduce material usage and transportation costs.
Advanced printing techniques and materials are also being employed to create more sustainable packaging. This reduces the need for multiple layers of plastic and allows for more efficient material utilization. Furthermore, the development of smart packaging, equipped with sensors and tracking technologies, can enhance supply chain transparency and reduce food waste by monitoring freshness and safety.
Data Analytics for Optimized Supply Chains
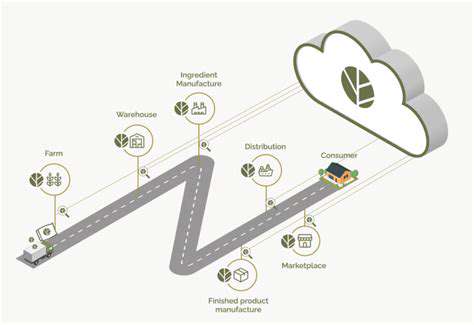
Data analytics is transforming supply chain management, enabling a more efficient and sustainable approach to food production and distribution. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, such as weather patterns, crop yields, and consumer demand, businesses can optimize logistics, reduce transportation costs, and minimize food waste. This data-driven approach allows for proactive adjustments to meet fluctuating demands and ensures that food reaches consumers efficiently and sustainably.
Renewable Energy Sources in Food Production
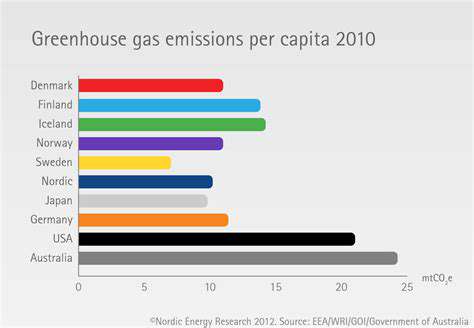
The transition to renewable energy sources is critical for reducing the carbon footprint of food production. Solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal energy can be integrated into farms and processing plants to power operations, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This shift towards renewable energy not only minimizes greenhouse gas emissions but also contributes to energy independence and cost savings for businesses.
Consumer Awareness and Engagement
Consumer awareness and engagement play a significant role in driving sustainable food practices. Transparency in food sourcing and production processes fosters consumer trust and encourages informed choices. Educational campaigns and informative labeling can empower consumers to make environmentally conscious decisions when purchasing food products. Educating consumers about the impact of their dietary choices, such as reducing meat consumption and opting for locally sourced produce, can further promote sustainable food systems.
Technological Advancements in Food Waste Reduction
Technological advancements are crucial in tackling the significant challenge of food waste. Innovations in food preservation techniques, such as advanced cold-chain logistics and modified atmosphere packaging, can extend shelf life and reduce spoilage. Smart refrigerators and food waste tracking apps can help consumers monitor and manage their food inventory more effectively, minimizing waste at the household level. Moreover, technologies that identify and categorize food waste can enable more effective resource recovery and composting practices.
Sustainable Food Packaging Design
Sustainable food packaging design is increasingly incorporating innovative materials and approaches to minimize environmental impact. The design process often considers material sourcing, recyclability, and biodegradability. Lightweight and reusable packaging options are gaining popularity to reduce material consumption and transportation costs. Furthermore, the development of innovative packaging designs, such as multi-functional containers and collapsible packaging, contributes to resource efficiency and waste reduction throughout the entire supply chain.
The Future of Sustainable Food Packaging: A Collaborative Effort
Innovative Materials and Design
The future of sustainable food packaging hinges on a fundamental shift towards innovative materials and design. This necessitates exploring bio-based polymers derived from renewable resources like corn starch or algae, alongside advancements in recycled and compostable plastics. Researchers are also focused on developing packaging with enhanced barrier properties, ensuring food safety and extending shelf life without compromising sustainability. Designing for minimal material usage and optimized form factors is crucial, reducing the overall environmental footprint of the packaging.
Beyond material innovation, design plays a critical role. Compact, stackable designs can significantly reduce transportation space, minimizing fuel consumption. Lightweight packaging further reduces the overall energy expenditure required for transportation, manufacturing, and eventual disposal. Clever use of multi-layered designs, incorporating barrier materials strategically, ensures product integrity while minimizing material waste.
Consumer Engagement and Education
Consumer engagement is paramount to driving the adoption of sustainable packaging. Educating consumers about the environmental impact of different packaging choices, highlighting the benefits of sustainable alternatives, and fostering a culture of responsible consumption are essential elements of this transition. Transparent communication about the lifecycle of packaging, from raw material sourcing to waste management, empowers consumers to make informed choices.
Clear labeling and certification schemes can help consumers identify and choose sustainable products. Furthermore, initiatives that reward eco-conscious purchasing choices, such as incentives and rebates, can encourage widespread adoption of sustainable packaging.
Technological Advancements in Manufacturing
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the manufacturing processes of sustainable food packaging. 3D printing, for instance, allows for customized packaging solutions, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. Additive manufacturing techniques can create intricate designs with minimal material use. These advancements not only enhance sustainability but also open up opportunities for personalized and localized food packaging, further minimizing transportation needs.
Automation and optimization of manufacturing processes can further reduce energy consumption and waste generation during production. Advanced sensors and real-time monitoring systems can ensure the quality and integrity of the packaging throughout the production chain, minimizing defects and maximizing resource utilization.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders
The transition to sustainable food packaging requires collaborative efforts between various stakeholders. Manufacturers need to partner with researchers and designers to develop innovative and sustainable materials and designs. Governments play a crucial role in setting regulations and providing incentives to encourage the adoption of sustainable practices. Consumer organizations can help raise awareness and educate consumers about the importance of sustainable choices.
Ultimately, a collaborative approach involving all stakeholders—from producers to consumers—is essential to creating a sustainable future for food packaging.
Recycling and Waste Management Infrastructure
Efficient recycling and waste management infrastructure are critical components of a sustainable food packaging system. Investment in advanced recycling technologies, specifically for complex multi-material packaging, is needed. Furthermore, improving public awareness and participation in recycling programs can substantially reduce the amount of packaging waste ending up in landfills. The development of robust and widely accessible waste sorting systems is crucial to ensure that materials are properly separated for optimal recycling.
Economic Viability and Market Trends
The economic viability of sustainable food packaging needs to be addressed. While the initial investment might seem higher for sustainable materials and processes, the long-term benefits, including reduced environmental impact, resource efficiency, and potential cost savings, are significant. Market trends suggest an increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. This creates a business opportunity for companies that adopt sustainable practices and cater to this growing market segment. Businesses that prioritize sustainability will likely experience increased brand loyalty and positive consumer perceptions.