Fuel Consumption and Efficiency
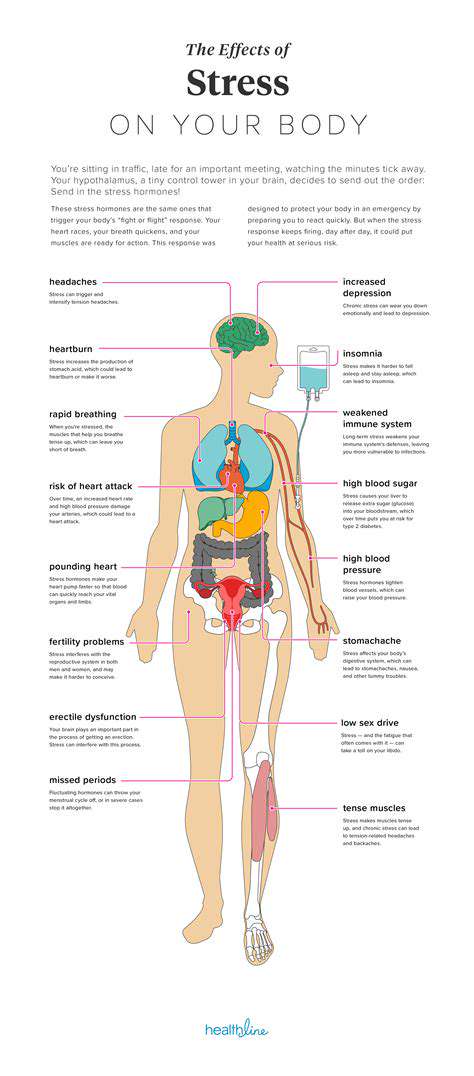
Understanding fuel consumption is crucial for both individual drivers and policymakers. Efficient fuel consumption directly impacts both personal costs and the environment. Lower fuel consumption translates to lower costs at the pump, which can save drivers significant money over time. Furthermore, minimizing fuel consumption contributes to reduced emissions of harmful greenhouse gases, thereby mitigating climate change.
Various factors influence fuel efficiency, including vehicle design, driving habits, and the type of fuel used. Innovative designs in engine technology and aerodynamics play a pivotal role in achieving higher fuel economy. Drivers can also significantly impact their fuel consumption through mindful driving practices, such as avoiding rapid acceleration and braking, maintaining a consistent speed, and keeping the vehicle properly maintained.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
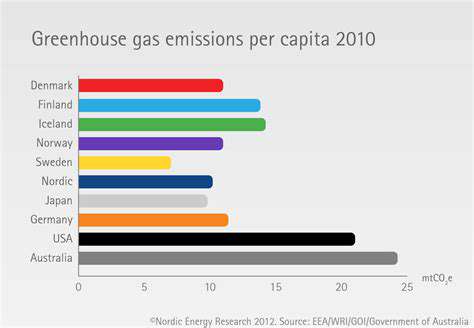
Greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), are a significant contributor to global warming and climate change. Transportation, particularly the use of fossil fuel-based vehicles, is a major source of these emissions. Understanding the relationship between fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions is critical to developing strategies for reducing environmental impact.
The emission of greenhouse gases from vehicles varies based on several factors, including the vehicle type, driving conditions, and fuel quality. Strategies for mitigating these emissions range from improving engine technology and fuel efficiency to promoting the use of alternative fuels and sustainable transportation options.
Impact on the Environment
The continuous burning of fossil fuels releases significant quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, exacerbating the effects of climate change. This leads to a cascade of environmental problems, including rising global temperatures, more frequent and severe weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems. Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach encompassing technological advancements, policy changes, and individual responsibility.
The environmental consequences of high fuel consumption are far-reaching. They extend beyond the immediate effects of air pollution, impacting water resources, biodiversity, and the overall health of the planet. The imperative to reduce fuel consumption and transition to more sustainable alternatives is paramount for preserving the environment for future generations.
Technological Advancements
Significant strides in automotive technology are focused on improving fuel efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Hybrid and electric vehicles, along with advancements in engine design and materials, are examples of these advancements. Innovative technologies, such as improved engine combustion systems and aerodynamic designs, are crucial for achieving significant reductions in fuel consumption. These technologies hold the potential to revolutionize transportation and significantly impact the environment.
Policy and Regulation
Governments worldwide are implementing policies and regulations aimed at promoting fuel efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These policies often include fuel economy standards, tax incentives for cleaner vehicles, and regulations on vehicle emissions. These measures are essential to fostering a shift towards sustainable transportation.
Regulations and standards play a critical role in shaping the automotive industry's direction. They incentivize manufacturers to develop more fuel-efficient vehicles, contributing to a reduction in harmful emissions and a more sustainable future.
Sustainable Transportation Solutions
The transition to sustainable transportation options is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of fuel consumption. Alternative fuels, such as biofuels and hydrogen, are being explored to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Public transportation, cycling, and walking are also essential components of a sustainable transportation system. Encouraging the use of these sustainable alternatives is a critical step toward a cleaner future.
Individual Responsibility
Individual choices regarding transportation can significantly impact fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Drivers can adopt more fuel-efficient driving habits, such as maintaining a consistent speed, avoiding rapid acceleration and braking, and ensuring proper tire inflation. Making conscious choices, such as carpooling, utilizing public transportation, or opting for electric vehicles, can have a substantial positive effect. By adopting these practices, individuals contribute to reducing their environmental footprint and promoting a more sustainable future. These choices ultimately contribute to a healthier planet for all.
The Impact on Biodiversity and Deforestation: Unintended Consequences of Transportation
Unintentional Habitat Fragmentation
The expansion of transportation networks, while crucial for economic development, often results in the fragmentation of natural habitats. Roads, railways, and pipelines carve through ecosystems, isolating populations of plants and animals. This isolation can lead to reduced genetic diversity within populations, making them more vulnerable to disease, environmental changes, and other threats. The loss of connectivity between once-continuous habitats disrupts migration patterns, breeding cycles, and the overall ecological balance, ultimately impacting biodiversity.
Further, the construction of these transportation corridors frequently involves clearing of significant tracts of land, contributing to a loss of vital biodiversity hotspots. The clearing, even for seemingly small projects, displaces existing species and disrupts delicate ecological relationships, which can have long-term consequences on the overall ecosystem health.
Increased Pollution and Emissions
Transportation systems, particularly those reliant on fossil fuels, are major contributors to air and noise pollution. The emissions from vehicles and industrial transportation contribute to climate change, impacting air quality, and harming human and animal health in surrounding areas. These pollutants can also affect the health of plants and animals directly, further exacerbating the challenges to biodiversity.
Furthermore, the noise generated by transportation infrastructure can disrupt the natural soundscapes of ecosystems, affecting animal communication, navigation, and stress levels. The constant noise pollution can disrupt the delicate balance of these environments, leading to a decline in biodiversity and affecting overall ecosystem health.
Infrastructure Development and Land Use Change
The construction of new transportation infrastructure often necessitates the conversion of natural habitats into developed land. This conversion can lead to a significant loss of biodiversity as existing ecosystems are replaced with roads, parking lots, and other infrastructure components. The removal of natural vegetation for construction activities also removes critical habitats for a wide range of species, making them vulnerable to extinction.
The alteration of land use patterns due to transportation can also disrupt water cycles and drainage patterns. These disruptions can have cascading effects on the local ecosystem, affecting the availability of water resources for plants and animals and potentially leading to habitat degradation.
Species Displacement and Extinction Risk
Transportation infrastructure can directly displace species from their habitats, particularly those with limited mobility or those with specific habitat requirements. Roads and railways can serve as barriers that prevent species from accessing crucial resources, including food and breeding grounds. This isolation can increase their vulnerability to extinction.
The fragmentation of habitats and the disruption of ecological processes driven by transportation can also make species more susceptible to invasive species, further increasing the risk of extinction and the decline of biodiversity in the region.
Impact on Migration Patterns
Transportation corridors can act as barriers to natural migration routes for many animal species. Roads and railways can fragment habitats, preventing animals from reaching their traditional breeding grounds or foraging areas. This disruption can lead to reduced genetic diversity and population size, ultimately impacting the long-term survival of species.
The disruption of migration patterns can also disrupt the delicate balance of predator-prey relationships, leading to cascading effects throughout the food web. This can have a significant impact on the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.
Economic and Social Consequences
The unintended consequences of transportation infrastructure development can have broader economic and social impacts. The loss of biodiversity can diminish the availability of natural resources and ecosystem services, impacting local economies that depend on these resources. Tourism and recreational activities can also be negatively affected by habitat loss and degradation. Furthermore, the disruption of ecological processes can affect human well-being and public health in the long run.
The social costs of transportation-related biodiversity loss can be significant, involving potential conflicts over land use, the displacement of communities, and the loss of cultural heritage linked to specific natural landscapes.
Climate Change and Carbon Emissions
The transportation sector is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, which exacerbate climate change. Increased transportation activity, particularly in fossil-fuel-based systems, releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to global warming and climate change, which can have profound impacts on biodiversity.
The changes in temperature and precipitation patterns driven by climate change can disrupt ecosystems, leading to habitat loss and species extinction. Transportation choices and policies that prioritize sustainable practices are crucial to mitigating the negative impacts of transportation on biodiversity and mitigating climate change.