Addressing the Challenges of Sustainable Beverage Packaging
Sustainable Practices in Agriculture
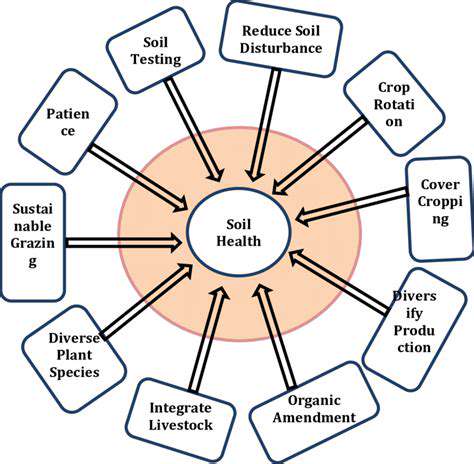
Farmers worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable agricultural methods to ensure long-term food security and environmental health. Techniques like crop rotation, organic pest control, and water conservation are becoming standard in progressive farming communities. These methods not only preserve soil quality but also reduce dependency on harmful chemicals, creating a healthier ecosystem for future generations. The shift towards sustainability isn't just an environmental imperative—it's becoming a business necessity as consumer preferences evolve.
Modern sustainable agriculture emphasizes the delicate balance between production needs and ecological preservation. By integrating natural processes into farming systems, practitioners create more resilient operations that can withstand climate variability and market fluctuations.
Economic Viability of Sustainable Practices
Transitioning to sustainable methods often requires upfront investment, but the financial benefits become clear over time. Farmers report significant savings on synthetic inputs after switching to organic alternatives. Market studies consistently show that sustainably grown products command higher prices, particularly in developed markets where consumers prioritize environmental responsibility. This price premium helps offset any initial productivity dips during the transition period.
The economic case strengthens further when considering risk mitigation. Sustainable farms typically experience fewer crop failures due to their diversified nature and healthier soils. Government incentives and certification programs provide additional financial support for those adopting these practices.
Environmental Impact of Conventional Agriculture
Traditional farming methods have left undeniable marks on our planet's ecosystems. Chemical runoff continues to threaten water supplies, while monoculture systems deplete soil nutrients at alarming rates. The biodiversity loss caused by intensive agriculture may represent one of our greatest environmental challenges, with some scientists warning of impending ecosystem collapse in key agricultural regions.
Soil degradation presents another critical issue, with some estimates suggesting we may have fewer than 60 harvests left in certain areas if current practices continue. The carbon footprint of conventional agriculture, from fertilizer production to food transportation, further exacerbates climate change concerns.
Social Implications of Sustainable Agriculture
Beyond environmental benefits, sustainable farming creates positive social ripple effects. Smallholder farmers gain greater control over their production systems, reducing vulnerability to corporate seed and chemical monopolies. Community-supported agriculture models foster direct connections between producers and consumers, rebuilding trust in food systems. These approaches often create more stable local economies and preserve traditional farming knowledge that might otherwise disappear.
Worker health improvements represent another significant advantage. Reduced exposure to toxic pesticides leads to fewer occupational illnesses, while diversified farm operations create year-round employment opportunities rather than seasonal work.
Technological Advancements in Sustainable Agriculture
Innovation is accelerating the sustainability transition across the agricultural sector. Soil sensors now provide real-time data on moisture and nutrient levels, allowing precise application of water and amendments. Drone technology enables farmers to monitor crop health across vast areas, identifying problems before they become widespread. These tools help maximize efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
Biotechnology also plays a role, with researchers developing crops that require fewer inputs or thrive in challenging conditions. When combined with traditional breeding techniques, these advances help create farming systems better adapted to local environments.
Policy and Regulatory Support for Sustainability
Governments worldwide are implementing policies to encourage sustainable agriculture. The European Union's Farm to Fork strategy sets ambitious targets for reducing chemical inputs, while various U.S. programs offer financial assistance for conservation practices. Emerging carbon credit markets create new revenue streams for farmers implementing climate-smart techniques. These policy measures help level the playing field between conventional and sustainable operations.
International agreements also shape agricultural practices, with sustainability criteria increasingly incorporated into trade agreements. This global policy environment pushes the entire sector toward more responsible production methods.
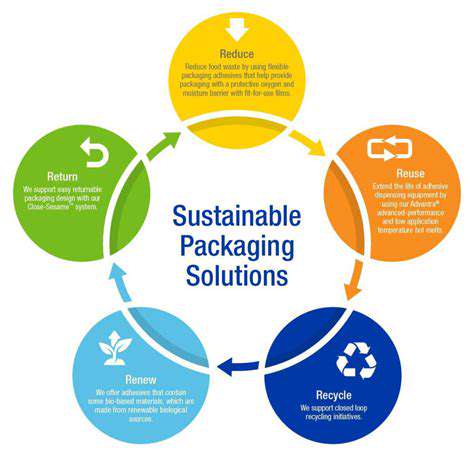
The Future of Sustainable Beverage Packaging

Sustainable Sourcing and Production
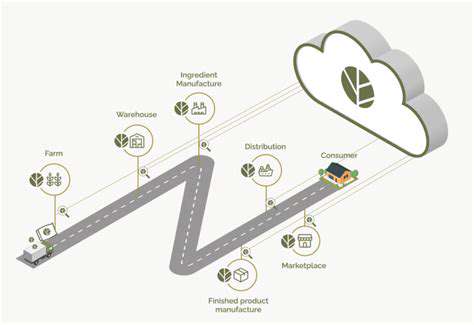
The beverage industry faces increasing pressure to address its environmental footprint through responsible sourcing. Leading companies now map their entire supply chains to identify and mitigate sustainability risks. Water stewardship has become particularly critical, with many operations implementing closed-loop systems that recycle up to 90% of process water. These measures not only reduce environmental impact but also future-proof businesses against resource scarcity.
Packaging innovation represents another frontier, with manufacturers experimenting with plant-based materials and edible coatings. Some startups have developed biodegradable bottles that decompose within months rather than centuries, offering promising alternatives to traditional plastics.
Technological Advancements
Cutting-edge technologies are revolutionizing sustainable beverage production. Advanced filtration systems now recover valuable byproducts from waste streams, creating circular production models. AI-powered quality control systems minimize product loss while ensuring consistent standards, reducing the environmental cost of rejected batches. These technological solutions help companies achieve both sustainability and efficiency goals simultaneously.
Renewable energy integration continues to expand, with solar-powered processing plants and biogas systems becoming more common. Some facilities now operate at net-zero energy, proving that decarbonization is achievable even in energy-intensive industries.
Consumer Demand and Engagement
Today's consumers wield significant influence over corporate sustainability strategies through their purchasing decisions. Research indicates that nearly 70% of consumers consider sustainability when selecting beverages, with younger demographics showing particular concern. This shift has forced brands to move beyond greenwashing and demonstrate genuine commitment through transparent reporting and third-party certifications.
Successful companies engage customers as partners in sustainability efforts. Deposit return schemes, refillable container programs, and upcycling initiatives all help consumers feel personally invested in environmental solutions. These approaches build brand loyalty while driving meaningful change.
Economic and Regulatory Factors
Financial realities are accelerating the industry's sustainability transition. The rising cost of virgin materials makes recycled alternatives increasingly attractive, while carbon pricing mechanisms internalize environmental costs. Progressive companies recognize that sustainability investments today will yield competitive advantages tomorrow as regulations tighten and consumer expectations rise.
Global policy frameworks continue to evolve, with extended producer responsibility laws shifting packaging waste management costs back to manufacturers. These regulatory pressures create strong incentives for innovation in sustainable packaging solutions.