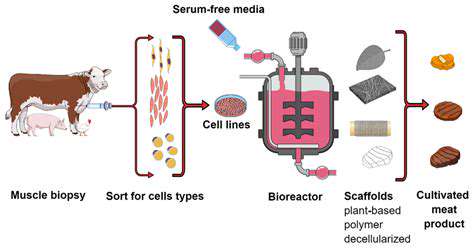
Cultivated Meat: A Revolution in Food Production
The emerging sector of cultivated meat, sometimes referred to as lab-cultured protein, represents a transformative approach to food manufacturing. Rather than relying on conventional livestock farming, this method grows muscle tissue directly from animal cells in bioreactors. This breakthrough could slash environmental damage while offering solutions to longstanding ethical dilemmas in animal husbandry.
By eliminating livestock rearing, cell-based meat production requires substantially less land and water while cutting greenhouse emissions by up to 90% compared to traditional methods. These efficiency gains suggest a viable pathway toward feeding our planet's expanding population without the ecological toll of conventional meat production.
Environmental Sustainability: The Core Benefit
The environmental argument for cultivated meat proves particularly compelling when examining current agricultural impacts. Standard meat production drives deforestation, contaminates waterways, and generates massive methane emissions. Cellular agriculture circumvents these issues by removing the requirement for grazing pastures and resource-intensive feed crops, fundamentally altering the ecological equation.
Water conservation represents another critical advantage, with cultured meat using approximately 80% less water than beef production. This becomes increasingly vital as climate change exacerbates water scarcity worldwide. The combined reductions in land use and carbon output position this technology as a potential game-changer for sustainable nutrition.
Ethical Dimensions of Cellular Agriculture
Beyond environmental gains, cultured meat addresses growing ethical concerns in food production. Industrial animal farming practices frequently compromise animal welfare, driving consumer demand for humane alternatives. Cellular agriculture offers a paradigm shift by producing meat without animal slaughter.
This innovation satisfies both ethical consumption and culinary preferences, providing meat's sensory experience without the associated moral compromises. The technology's focus on cell cultivation rather than whole organisms suggests a possible future where meat consumption aligns with compassionate values.
Technological Progress and Market Potential
Breakthroughs in tissue engineering are rapidly advancing cultured meat's viability. Research teams worldwide are refining techniques to enhance product quality while reducing production costs. Current developments suggest that price parity with conventional meat may become achievable within this decade, dramatically expanding accessibility.
The sector's growth trajectory indicates that cultured proteins could capture significant market share by 2035. As production scales and technologies mature, these products may transform from niche offerings to mainstream dietary staples, potentially reshaping global protein supply chains.
Overcoming Development Challenges
Despite progress, cultured meat faces several obstacles. Production costs remain prohibitively high for most consumers, requiring further optimization of cell culture media and bioreactor efficiencies. Regulatory frameworks also need development to ensure product safety while facilitating market entry.
Consumer perception presents another critical hurdle. Effective communication about the technology's benefits and safety will be essential for widespread adoption. Ongoing research and transparent industry practices will prove crucial in building public trust and accelerating market penetration.
Beyond Meat: Expanding the Cellular Agriculture Portfolio
Beyond Meat's Growth Strategy
Beyond Meat's market expansion relies on diversifying its protein alternatives beyond initial plant-based offerings. The company actively explores novel applications in cellular agriculture through strategic partnerships with biotech firms and academic institutions. These collaborations aim to develop advanced meat analogs that replicate not just texture but also complex flavor profiles and nutritional compositions.
Strategic alliances form the cornerstone of this expansion, providing access to specialized knowledge, production technologies, and distribution networks. Such partnerships will likely determine the company's ability to scale operations and maintain competitiveness in the evolving alternative protein sector.
Cellular Agriculture's Systemic Impact
The emergence of cellular agriculture could fundamentally restructure global food systems by offering sustainable alternatives to conventional livestock production. While the technology promises reduced environmental impact and enhanced product consistency, significant barriers remain regarding production scalability and consumer acceptance.
Scaling Production: Technical Hurdles
Transitioning from laboratory to industrial-scale production presents formidable engineering challenges. Companies must develop cost-effective bioreactor systems and sustainable growth media while addressing energy requirements and waste management. Beyond Meat and similar enterprises face the dual challenge of technological innovation and economic viability as they scale operations.
The potential market for cultured protein products could exceed $25 billion by 2030, representing both enormous opportunity and significant technical and financial risk for industry pioneers.
Building Consumer Trust
Market success will depend largely on public perception and acceptance. Companies must educate consumers about production methods, safety protocols, and environmental benefits while addressing concerns about lab-grown foods. Transparent marketing and clear labeling will be essential for gaining consumer confidence in these novel products.
Future Positioning
Beyond Meat's established brand recognition provides a competitive advantage in the emerging cellular agriculture market. The company's ability to integrate new technologies with existing product lines while maintaining quality standards will determine its long-term market position. Continued innovation and adaptation will be necessary as the alternative protein landscape evolves.
The Future of Food: Investment and Collaboration

Investment Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture
Modern agricultural investment increasingly prioritizes sustainability alongside profitability. Forward-thinking investors recognize that environmentally sound practices often yield superior long-term returns while mitigating ecological damage. This shift drives funding toward regenerative techniques, precision farming, and climate-adaptive crop development.
Methods like cover cropping and biological pest control demonstrate how ecological principles can enhance both productivity and sustainability. Strategic investments in these areas promise to create more resilient food systems while generating stable financial returns.
Technological Innovations Reshaping Agriculture
Digital agriculture technologies are transforming food production through data-driven optimization. Satellite imaging and IoT sensors enable precise resource application, while automated systems improve irrigation efficiency and reduce labor costs. These innovations collectively enhance yields while minimizing environmental impacts.
Genetic crop improvements, when responsibly developed and regulated, offer solutions to pressing agricultural challenges. Drought-resistant and pest-tolerant varieties could prove critical for maintaining food security in climate-vulnerable regions. Meanwhile, controlled environment agriculture techniques like vertical farming demonstrate how innovation can dramatically reduce land and water requirements.
Advances in food preservation and distribution technologies also play a vital role in reducing waste and improving accessibility. Smart packaging materials and blockchain-enabled supply chains enhance food safety while extending shelf life, particularly important for perishable goods in developing markets.
Emerging Investment Opportunities
The evolving food sector presents diverse investment prospects across the value chain. Companies developing sustainable production methods and alternative proteins represent particularly attractive opportunities as consumer preferences shift. The growing demand for organic and locally-sourced products has created thriving niche markets with premium pricing potential.
Food technology ventures are attracting significant capital, particularly those addressing critical challenges like food waste reduction and nutritional enhancement. Investors can find promising opportunities in companies bridging the gap between technological innovation and practical agricultural applications. The intersection of agriculture and digital technology continues to yield novel business models with strong growth potential.