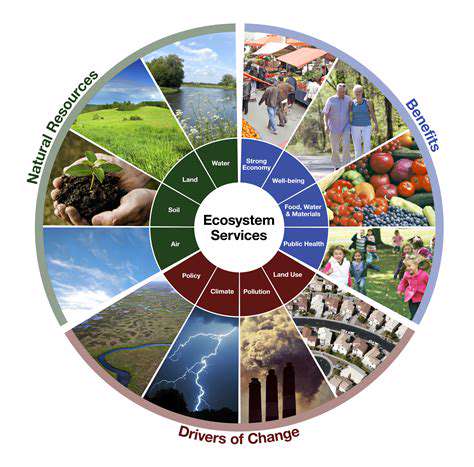
The Imperative for Sustainable Supply Chains in Food Production
Optimizing Efficiency for Environmental Sustainability
Sustainable supply chains in food production demand a radical transformation toward maximizing efficiency at every stage of the value chain. Implementing cutting-edge technologies and innovative methods can drastically cut waste, conserve resources, and boost operational performance from farm to consumer. Streamlining workflows, shortening transport routes, and switching to eco-friendly packaging allow companies to shrink their environmental impact while supporting a greener food ecosystem. A comprehensive life-cycle analysis—from raw material sourcing to end-user consumption—helps pinpoint and address ecological concerns at each phase.
Precision agriculture is revolutionizing farm management. By leveraging real-time data, growers can fine-tune irrigation, fertilizer use, and pest control—slashing environmental harm while increasing output. This dual benefit of ecological preservation and economic gain creates a compelling case for widespread adoption. The approach demonstrates how technological advancement can align profitability with planetary health.
Building Resilience Through Diversification and Local Partnerships
Food systems gain durability through diversified supplier networks and robust local collaborations. Relying on single-source providers leaves supply chains exposed to climate disasters and geopolitical upheavals. A multi-sourced network offers critical flexibility, ensuring consistent food availability despite disruptions. Partnering with regional producers not only strengthens local economies but also reduces carbon emissions by minimizing long-haul transportation.
Community-based farming initiatives foster direct relationships between food creators and consumers. This transparency empowers shoppers to make ethically informed choices while preserving regional culinary heritage. Local collaborations also protect biodiversity by encouraging cultivation of native crops using traditional methods—an often-overlooked benefit of shortened supply chains.
Promoting Transparency and Ethical Practices Throughout the Chain
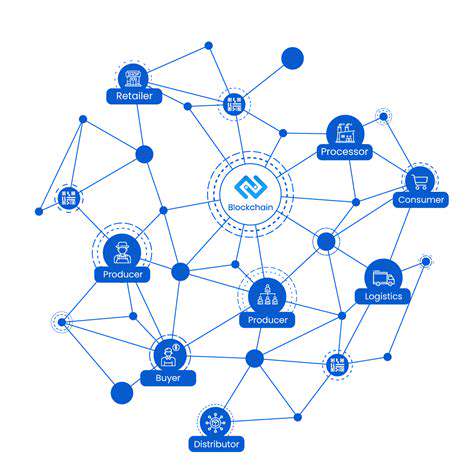
Modern consumers demand complete visibility into their food's journey. Ethical sourcing policies and detailed production disclosures allow buyers to support responsible brands. This level of openness not only builds consumer confidence but also helps companies identify and rectify supply chain shortcomings. Blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful tool for verifying product origins and labor conditions.
Fair treatment of agricultural workers remains non-negotiable. Ensuring living wages, safe working conditions, and humane treatment across the supply chain demonstrates genuine corporate responsibility. Companies that prioritize these values earn customer loyalty while contributing to systemic industry improvements.
Promoting Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Enhancing Crop Resilience
Modern agriculture focuses on developing hardy crops capable of withstanding droughts, floods, and temperature extremes. Strategic crop rotation and polyculture planting create natural defenses against pests and diseases, reducing chemical dependency. These methods preserve ecological balance while ensuring stable yields despite climatic volatility.
Improving Soil Health
Vital agricultural reforms begin underground. No-till techniques prevent topsoil loss while cover crops act as living mulch—suppressing weeds and enriching earth with organic matter. These regenerative practices rebuild degraded soils, increasing farmland productivity without synthetic inputs. Healthy soil ecosystems naturally retain moisture and nutrients, forming the foundation for sustainable food production.
Minimizing Water Usage
With freshwater supplies dwindling globally, precision irrigation systems deliver targeted hydration to plant roots—eliminating the wastefulness of flood irrigation. Rainwater capture systems provide drought-proof water sources while easing pressure on municipal supplies. Such innovations demonstrate how technology can reconcile agricultural needs with environmental limits.
Integrating Livestock Management
Regenerative grazing patterns allow pastures to rejuvenate between grazing cycles, preventing land degradation. Advanced manure processing converts waste into renewable fertilizer, closing nutrient loops on farms. These closed-loop systems dramatically reduce pollution while maintaining productivity.
Promoting Biodiversity
Agricultural landscapes flourish when designed as ecosystems rather than monocultures. Flowering borders attract pollinators while predatory insects keep pests in check. This biological pest control reduces pesticide needs while supporting threatened species. Diverse farms prove more resilient to climate shocks than single-crop operations.
Utilizing Renewable Energy
Solar-powered irrigation and wind-driven processing equipment are transforming farms into clean energy hubs. These transitions cut operational costs while eliminating greenhouse gas emissions. Some forward-thinking operations now generate surplus renewable energy for their communities.
Implementing Traceability
Blockchain-enabled tracking provides immutable records from seed to shelf. This radical transparency deters unethical practices while empowering conscious consumers. Detailed production histories help brands differentiate themselves in an increasingly values-driven marketplace.

Engaging Stakeholders for Collaborative Solutions
Understanding Stakeholder Needs
Effective collaboration begins with deep understanding of all affected parties. Comprehensive stakeholder mapping reveals hidden concerns and unexpected synergies. Face-to-face interviews often uncover priorities that surveys miss—valuable insights for shaping inclusive solutions.
Creating Clear Communication
Multi-channel outreach ensures no voice goes unheard. Tailored messaging—whether through social media, town halls, or printed materials—builds genuine engagement. Interactive dashboards can provide real-time project updates while soliciting continuous feedback.
Building Trust
Trust accrues through consistent action, not empty promises. Publicly documenting follow-through on commitments proves more persuasive than mission statements. Advisory councils with rotating membership prevent stakeholder fatigue while maintaining diverse input.
Fostering Collaboration
Co-design workshops transform passive observers into active partners. Shared problem-solving sessions often yield innovative solutions that elude top-down approaches. Digital whiteboarding tools enable remote participants to contribute equally to in-person teams.
Providing Support
Capacity-building workshops equip stakeholders with needed skills. Multilingual resources and accessibility accommodations demonstrate genuine inclusion. Some organizations provide stipends to enable participation from economically disadvantaged groups.
Evaluating Strategies
Quarterly impact assessments keep engagement efforts relevant. Anonymous feedback channels encourage candid critiques that drive meaningful improvements. Successful programs evolve their approaches based on measurable outcomes rather than assumptions.