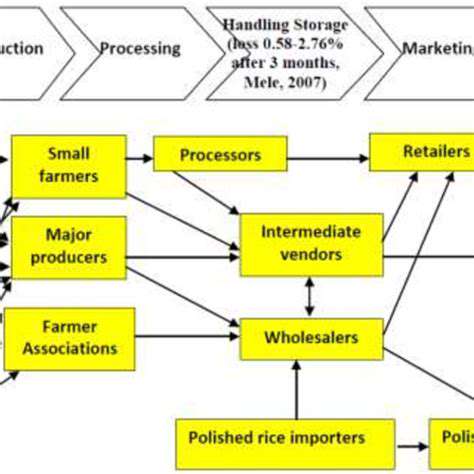
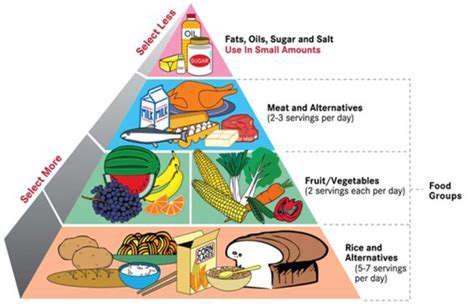
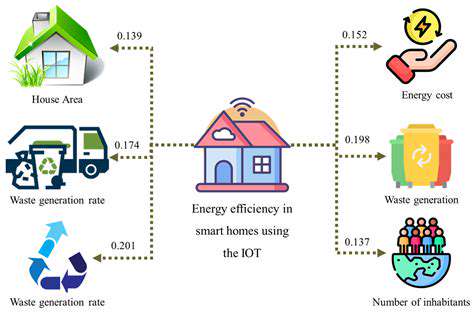
A Sustainable Alternative
With the world's population expanding rapidly, traditional livestock farming struggles to meet the escalating demand for protein. Cultivated meat, produced through cellular agriculture, presents a groundbreaking solution by replicating animal muscle tissue growth in controlled lab settings. This method bypasses the need for industrial animal farming, offering substantial environmental benefits such as lowered greenhouse gas emissions, reduced deforestation, and minimized water consumption.
Another critical advantage lies in public health. By eliminating animal-human contact in production, cultivated meat significantly decreases the risk of zoonotic disease transmission—a pressing concern in today's world of emerging pathogens.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
Conventional meat production remains one of the most environmentally damaging industries. The staggering land requirements for grazing, methane emissions from livestock, and excessive water usage create an unsustainable ecological burden. In contrast, lab-grown meat requires up to 95% less land and 78% less water according to recent studies, presenting a dramatically reduced environmental footprint.
Cost and Accessibility Challenges
The current price point of cultivated meat remains its primary barrier to mainstream adoption. As a fledgling technology, production costs remain high, though industry experts predict substantial reductions within the next five years. With improved bioreactor efficiency and scaling of production facilities, prices are expected to reach parity with conventional meat by 2030. Singapore's recent approval of lab-grown chicken products marks a significant step toward commercial viability.
Ethical Dimensions
The ethical landscape of cultivated meat presents both clear advantages and complex questions. While eliminating animal slaughter addresses significant welfare concerns, philosophical debates persist regarding the use of animal cells and the definition of meat. Some ethicists argue that cultivated products represent a moral middle ground, satisfying meat demand without requiring animal suffering.
The Future of Food Production
Cultivated meat stands poised to transform global food systems, offering a viable solution to the protein crisis while addressing environmental sustainability. Though challenges remain in scaling production and gaining consumer acceptance, the technology's potential is undeniable. Recent breakthroughs in scaffolding techniques and serum-free growth media suggest we're approaching a tipping point for this innovative food technology.
Investments from major food corporations and governments indicate growing confidence in cultivated meat's role in creating a more sustainable and ethical food future.

Challenges and Future Considerations

Technological Advancements and Integration
The accelerating pace of technological innovation brings both revolutionary potential and complex implementation challenges. Successful adoption of AI and machine learning systems requires careful navigation of data security protocols and workforce transition strategies. Organizations must invest in continuous training programs to bridge the skills gap created by these emerging technologies.
Resource Management for Sustainability
Sustainable resource allocation has become non-negotiable in modern operations. Forward-thinking organizations are implementing circular economy principles, where waste streams become inputs for other processes. Energy-efficient bioreactors and renewable energy-powered facilities are setting new standards for environmental responsibility in food production.
Data Governance in the Digital Age
With the explosion of production data, implementing robust data governance frameworks has become critical for operational success. Advanced encryption methods and blockchain-based tracking systems are emerging as essential tools for maintaining data integrity throughout complex supply chains.
Collaborative Innovation Models
The complexity of modern food systems demands unprecedented levels of collaboration. Cross-industry partnerships between biotech firms, food manufacturers, and academic institutions are accelerating innovation. Open-source platforms for research sharing are demonstrating remarkable success in solving shared technical challenges.
Ethical Frameworks for Emerging Technologies
As biotechnology advances, the development of comprehensive ethical guidelines has become imperative. Industry leaders are establishing ethics review boards to evaluate new production methods and address consumer concerns about genetic engineering and cellular agriculture.
Investment Landscape Evolution
The alternative protein sector has seen explosive growth in venture capital. Strategic investment in infrastructure and talent development is proving crucial for scaling operations. Governments worldwide are implementing supportive policies, with the EU recently establishing a €200 million fund for cellular agriculture research.
Adapting to Market Dynamics
The ability to pivot quickly has become a defining characteristic of successful food tech companies. Consumer education initiatives are proving vital for overcoming initial skepticism, with taste demonstrations and transparent labeling helping build market trust.