The Emerging Role of Bioactive Compounds in Nutrition
The Growing Importance of Bioactive Compounds
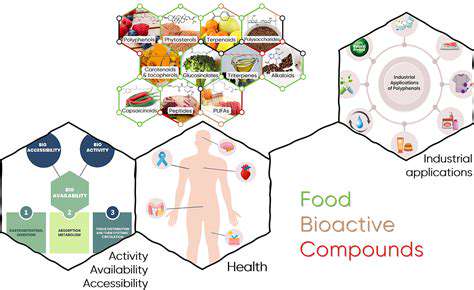
Bioactive compounds exist naturally across diverse food sources, plants, and microbial organisms. Nutrition scientists now emphasize their significance in promoting health beyond mere sustenance. Current evidence suggests these substances may be pivotal in disease prevention and management, driving extensive research in both nutritional science and pharmaceutical development.
Investigations into bioactive components have deepened our comprehension of diet-health-disease interconnections. Researchers continue examining their multifaceted actions, ranging from cellular modulation to immune system regulation.
Mechanisms of Action
Bioactive compounds influence human physiology through diverse and sophisticated pathways. Many engage with cellular receptors, initiating biochemical sequences that yield health benefits. The intricate relationship between these compounds and bodily systems represents a primary research focus.
Additionally, certain bioactive agents modify gut microbiota composition, significantly affecting overall health. Ongoing studies aim to clarify these microbe-compound interactions and their health implications.
Dietary Sources and Bioavailability
Recognizing food sources abundant in bioactive compounds is essential for nutritional planning. Common examples include fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and various spices. A critical research area involves determining bioavailability - how efficiently the body processes and utilizes these compounds.
Applications in Health and Nutrition
Potential applications for bioactive compounds span disease prevention, healthy aging, and general wellness enhancement. Scientific optimism exists regarding their potential for developing individualized health management solutions.
From supplemented foods to specialized nutrition products, these natural substances offer broad applications. Continued research promises to reveal additional health benefits.
Future Directions and Challenges
Key challenges facing this field include standardizing extraction techniques, maintaining quality consistency, and establishing consumption safety protocols. Further investigation remains crucial for understanding the complex dynamics between bioactive compounds and human physiology.
Future studies will likely emphasize personalized supplementation approaches, accounting for genetic and individual variability. This requires advanced knowledge of compound effects across different populations.
Tailoring Nutrition Strategies with Bioactive Compounds
Individualized Dietary Approaches
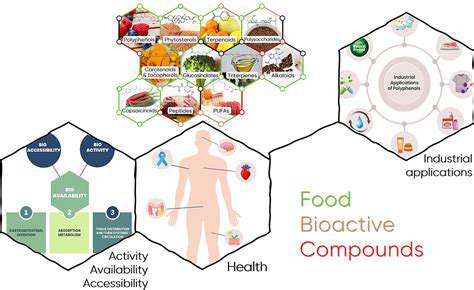
Customized nutrition planning proves essential for achieving optimal health results. This requires evaluating multiple factors including age, biological sex, activity patterns, health status, and food preferences. Personalized nutrition acknowledges the limitations of generalized dietary advice in meeting individual requirements. Qualified nutrition professionals can assess personal circumstances to develop targeted plans addressing specific objectives like weight control, disease prevention, or physical performance enhancement.
Nutritional requirements evolve throughout life stages, necessitating adaptable approaches. This customized methodology empowers individuals to make informed decisions supporting their unique health circumstances.
Considering Lifestyle Factors
Daily routines, occupational demands, and social obligations significantly influence eating behaviors. Effective nutrition planning must account for these practical considerations, identifying potential obstacles like limited food access or preparation time constraints.
Cultural and social dimensions also warrant consideration, as traditional food practices often shape dietary patterns. Incorporating these elements enhances plan adherence and sustainability.
Effective nutrition strategies should address stress-related eating patterns. Dietary plans must maintain sufficient flexibility to accommodate life's unpredictable nature.
Ultimately, personalized nutrition respects individual differences, creating enjoyable and sustainable approaches that maximize health benefits.

The Impact of Bioactive Compounds on Specific Health Conditions
Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Bioactive components present in various foods contribute significantly to cardiovascular maintenance. Their antioxidant properties and nutrient profiles support heart health by regulating cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and vascular function. Research demonstrates reduced cardiovascular risks associated with bioactive-rich diets.
Specific compounds like berry flavonoids actively counteract oxidative damage, offering protection against cardiovascular deterioration.
Effect on Neurological Function
Current studies suggest certain bioactive agents may support brain health. Compounds such as polyphenols show potential for protecting against cognitive decline and neurological disorders through anti-inflammatory effects and neural growth promotion.
Role in Anti-Aging Processes
Bioactive compounds demonstrate promising anti-aging potential by combating cellular oxidation. This protective mechanism may delay age-related health decline, with studies linking their consumption to maintained physical and cognitive function in aging populations.
Influence on Gut Health
These compounds promote beneficial gut microbiota growth, enhancing digestive efficiency and immune response. Their prebiotic effects contribute to maintaining optimal gut balance and reducing gastrointestinal disorder risks.
Impact on Cancer Prevention
Certain bioactive agents exhibit cancer-protective qualities through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions that may inhibit malignant cell development and progression.
Management of Metabolic Disorders
Bioactive compounds show potential in addressing metabolic conditions like diabetes and obesity by improving insulin response and reducing inflammatory markers associated with these disorders.