Types of Plant-Based Cheeses: A Flavorful Journey
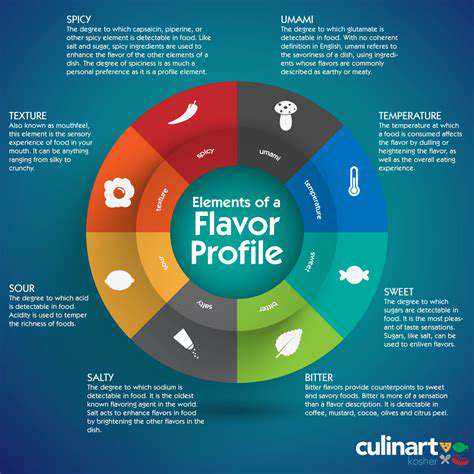
Plant-based cheeses have moved far beyond their early iterations, now offering a rich tapestry of textures and flavors that rival traditional dairy. From silky cashew-based spreads perfect for crackers to aged almond cheeses with a bold bite, the diversity is staggering. This section explores how different bases like coconut, soy, and even root vegetables create unique sensory experiences.
What makes these alternatives truly remarkable is their ability to capture the essence of cheese while offering novel taste dimensions. The subtle sweetness of cashew-based brie contrasts beautifully with the sharp tang of fermented soy varieties, proving plant-based options can stand on their own rather than simply mimicking dairy.
The Alchemy of Texture: Crafting Dairy-Free Perfection
Recreating the mouthfeel of traditional cheese requires scientific precision. Artisans employ techniques like controlled fermentation and specialized aging processes to develop complexity. The breakthrough comes from understanding how plant proteins interact with natural thickeners like agar-agar or carrageenan to create that coveted stretch and melt.
Temperature control proves crucial throughout production - too warm and the texture becomes gummy, too cold and flavors fail to develop. The most successful products achieve that elusive balance between creamy indulgence and structural integrity that holds up in cooking applications.
Flavor Innovation: Beyond Imitation
The modern plant-based cheese movement has shifted from replication to reinvention. Producers now highlight the natural flavors of their base ingredients while introducing innovative seasoning blends. Smoked paprika-infused varieties or truffle-dusted wheels demonstrate how these products can surpass their dairy counterparts in creativity.
Environmental Impact and Ethical Production
Consumers increasingly choose plant-based options for their smaller ecological footprint. A single pound of cashew cheese requires significantly less water and land than traditional dairy cheese, while generating fewer greenhouse gases. Many producers now prioritize regenerative agriculture practices, creating positive feedback loops within their supply chains.
Ethical considerations extend beyond animals to include fair labor practices and support for small-scale farmers. The most conscientious brands build their business models around these values, creating products that satisfy both palate and principles.
The Cutting Edge of Dairy-Free Cheese
Emerging technologies promise even more exciting developments. Precision fermentation allows for creating dairy-identical proteins without animals, while novel aging techniques borrowed from traditional cheesemaking bring unprecedented depth. The next frontier includes regionally-inspired varieties that reflect local terroir, much like fine wines.
Foundations of Flavor: Selecting Your Plant-Based Cheese Base
The Critical Importance of Base Selection
Your base ingredient determines the entire character of your plant-based cheese. Like choosing grapes for wine, this decision impacts texture, flavor profile, and culinary performance. Nutritionally, different bases offer varying protein content and healthy fats, allowing for targeted dietary benefits.
Exploring Base Ingredients
Each base brings unique advantages:- Cashews create luxurious, fatty textures ideal for soft cheeses- Almonds offer delicate flavors perfect for aged varieties- Oats provide neutral bases for strongly flavored additions- Soy delivers high protein content for firmer textures
Preparation Techniques Matter
Proper soaking times, blending methods, and straining processes dramatically affect results. For nut-based cheeses, soaking for 8-12 hours activates enzymes that improve digestibility while creating creamier textures. Temperature-controlled fermentation develops complex flavors over time, much like traditional cheesemaking.
The Science of Creaminess: Mastering Emulsification
Emulsification Fundamentals
Successful emulsification creates that magical mouthfeel we associate with premium cheeses. The process involves breaking fat molecules into microscopic droplets suspended in water-based solutions. This scientific principle explains why some plant-based cheeses achieve that perfect melt while others remain grainy.
Natural Emulsifiers in Action
Sunflower lecithin has emerged as a game-changer, allowing for smooth textures without soy. Psyllium husk provides fiber-rich thickening, while aquafaba (chickpea brine) offers egg-like binding properties. The key lies in balancing these emulsifiers with the right acidity levels to prevent separation during heating.